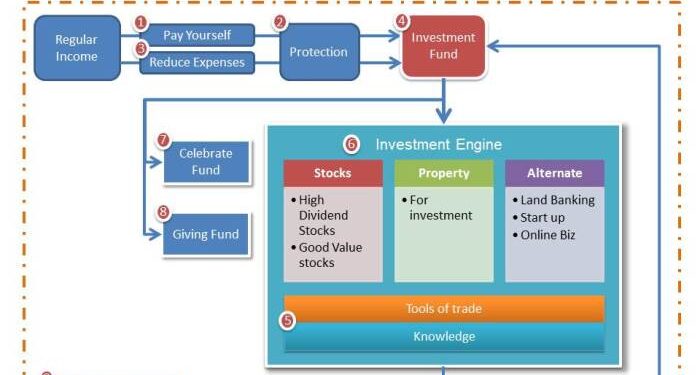
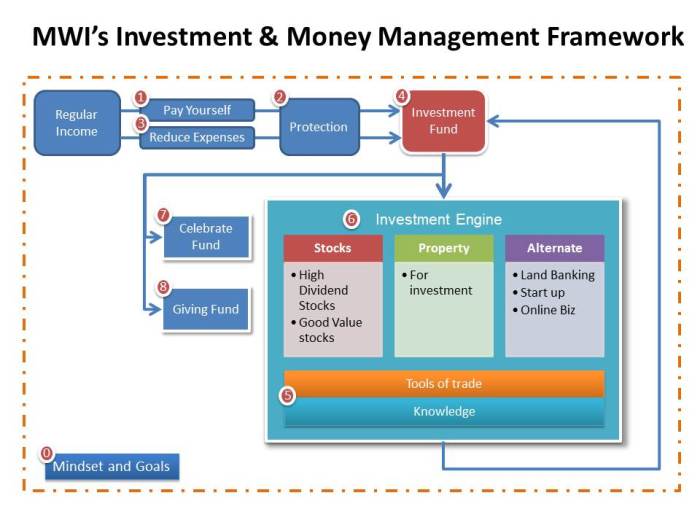
Delving into the world of institutional investors and their money wealth management techniques opens up a realm of possibilities. From asset allocation strategies to risk management tactics, this topic offers a deep dive into the financial strategies used by major players in the market.
Let's explore the intricate web of investment decisions and regulatory compliance that shape the landscape of wealth management for institutional investors.
Overview of Institutional Investors

Institutional investors play a crucial role in the financial market, managing large sums of money on behalf of various entities. These investors are typically organizations such as pension funds, insurance companies, mutual funds, and hedge funds.
Types of Institutional Investors
- Pension Funds: Pension funds manage assets to provide retirement benefits for employees. They focus on long-term growth and income generation to meet future obligations.
- Insurance Companies: Insurance companies invest premiums collected from policyholders to generate returns and ensure they have sufficient funds to pay out claims.
- Mutual Funds: Mutual funds pool money from individual investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of assets, aiming to achieve capital appreciation and income.
- Hedge Funds: Hedge funds are alternative investment funds that employ a variety of strategies to generate high returns for their investors, often with higher risk levels.
Money Management Techniques
Institutional investors utilize various money management techniques to effectively manage their wealth and achieve their financial goals.
Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation is a crucial component of money management for institutional investors. It involves distributing investments across different asset classes to achieve a balance between risk and return. Some common asset allocation strategies employed by institutional investors include:
- Strategic Asset Allocation: This long-term approach involves setting target allocations for different asset classes based on the investor's risk tolerance and investment objectives.
- Tactical Asset Allocation: This dynamic approach involves making short-term adjustments to the portfolio based on market conditions and opportunities.
- Dynamic Asset Allocation: This strategy involves actively managing asset allocation based on changing market conditions and economic outlook.
Diversification in Wealth Management
Diversification is a key principle in wealth management that involves spreading investments across a variety of assets to reduce risk. Institutional investors understand the importance of diversification in achieving a well-balanced portfolio. By diversifying their investments, institutional investors can minimize the impact of volatility in any single asset or market segment.
This helps to protect their wealth and potentially improve overall returns.
Risk Management Strategies
Institutional investors employ various risk management strategies to protect their investment portfolios and achieve long-term financial goals. These strategies help them assess and mitigate risks effectively, ensuring a balanced and diversified approach to wealth management.
Diversification
Diversification is a key risk management strategy used by institutional investors. By spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and regions, they reduce the impact of market fluctuations on their overall portfolio. This helps in minimizing the risk of significant losses in case one sector or asset class underperforms.
- Allocating assets across equities, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments.
- Investing in both domestic and international markets to reduce country-specific risks.
- Ensuring a mix of high-risk, high-return investments and low-risk, stable assets.
Risk Assessment and Monitoring
Institutional investors continuously assess and monitor risks in their investment portfolios to make informed decisions and adjustments as needed. They use sophisticated risk management tools and analytics to identify potential threats and opportunities, allowing them to react swiftly to changing market conditions.
- Utilizing risk metrics such as Value at Risk (VaR) and stress testing to measure portfolio risk.
- Regularly reviewing and rebalancing the portfolio to maintain desired risk levels.
- Implementing stop-loss orders and other risk mitigation techniques to limit downside exposure.
Active Portfolio Management
Active portfolio management is another risk management strategy employed by institutional investors. By actively monitoring and adjusting investments based on market trends, economic indicators, and risk factors, they aim to maximize returns while minimizing potential losses.
- Engaging in market research and analysis to identify investment opportunities and threats.
- Making tactical asset allocation changes based on short-term market conditions.
- Utilizing hedging strategies such as options and futures to protect against downside risks.
Investment Strategies
Investment strategies are crucial for institutional investors to maximize returns and manage risks effectively
Active vs. Passive Investment Strategies
Active investment strategies involve frequent buying and selling of assets with the goal of outperforming the market. This approach requires in-depth research, analysis, and market timing. On the other hand, passive investment strategies involve holding a diversified portfolio to mirror a specific market index, aiming to match its performance rather than beat it.
Passive strategies often have lower costs and are less time-intensive compared to active strategies.
- Active strategies:
- Involve higher trading activity and require skilled investment professionals.
- Seek to generate alpha by exploiting market inefficiencies.
- Can be riskier due to higher volatility and concentration of holdings.
- Passive strategies:
- Offer lower fees and expenses compared to active strategies.
- Provide broad market exposure and diversification.
- Are more suitable for long-term investors seeking steady returns.
The choice between active and passive strategies depends on the investment goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
Role of Market Research and Analysis
Market research and analysis play a crucial role in shaping investment decisions for institutional investors. By conducting thorough research and analysis, investors can identify opportunities, assess risks, and make informed investment choices.
- Market research involves studying market trends, economic indicators, and industry developments to anticipate potential opportunities and threats.
- Financial analysis helps in evaluating the financial health and performance of companies, sectors, or asset classes to make sound investment decisions.
- Risk analysis assesses the potential risks associated with an investment and helps in implementing risk management strategies to protect the portfolio.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of wealth management for institutional investors. These investors are required to adhere to a set of regulations and guidelines set forth by governing bodies to ensure transparency, accountability, and investor protection.
Regulatory Requirements for Institutional Investors
- Institutional investors must comply with regulations such as SEC rules, anti-money laundering laws, and fiduciary responsibilities.
- They are required to disclose their investment activities, financial statements, and potential conflicts of interest.
- Compliance with regulations helps maintain market integrity and investor confidence in the financial system.
Impact on Investment Decisions
- Compliance with regulations can impact investment decisions by limiting certain investment strategies or imposing restrictions on specific asset classes.
- Institutional investors may need to allocate resources to ensure compliance, which can affect overall portfolio performance.
- Failure to comply with regulations can result in legal repercussions, fines, or reputational damage.
Importance of Ethical Considerations
- Ethical considerations play a significant role in wealth management practices, guiding institutional investors to make responsible and sustainable investment choices.
- Adhering to ethical standards helps build trust with clients, stakeholders, and the broader community.
- Ethical wealth management practices contribute to long-term value creation and positive social impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the strategies and practices employed by institutional investors in managing wealth are crucial elements in achieving long-term financial success. By understanding the nuances of money management techniques and risk mitigation strategies, one can navigate the complex world of institutional investments with confidence and expertise.
FAQ Corner
What are some common money management techniques used by institutional investors?
Institutional investors often employ strategies like asset allocation, diversification, and market analysis to manage large sums of money effectively.
How do institutional investors assess and mitigate risks in their investment portfolios?
Institutional investors conduct thorough risk assessments and utilize various risk management strategies such as hedging and diversification to mitigate potential financial risks.
Why is regulatory compliance important for institutional investors?
Regulatory compliance ensures that institutional investors operate within legal boundaries, safeguarding investor interests and maintaining market integrity.